IN THIS ARTICLE
what is DC power?
// WHAT IS DC POWER?
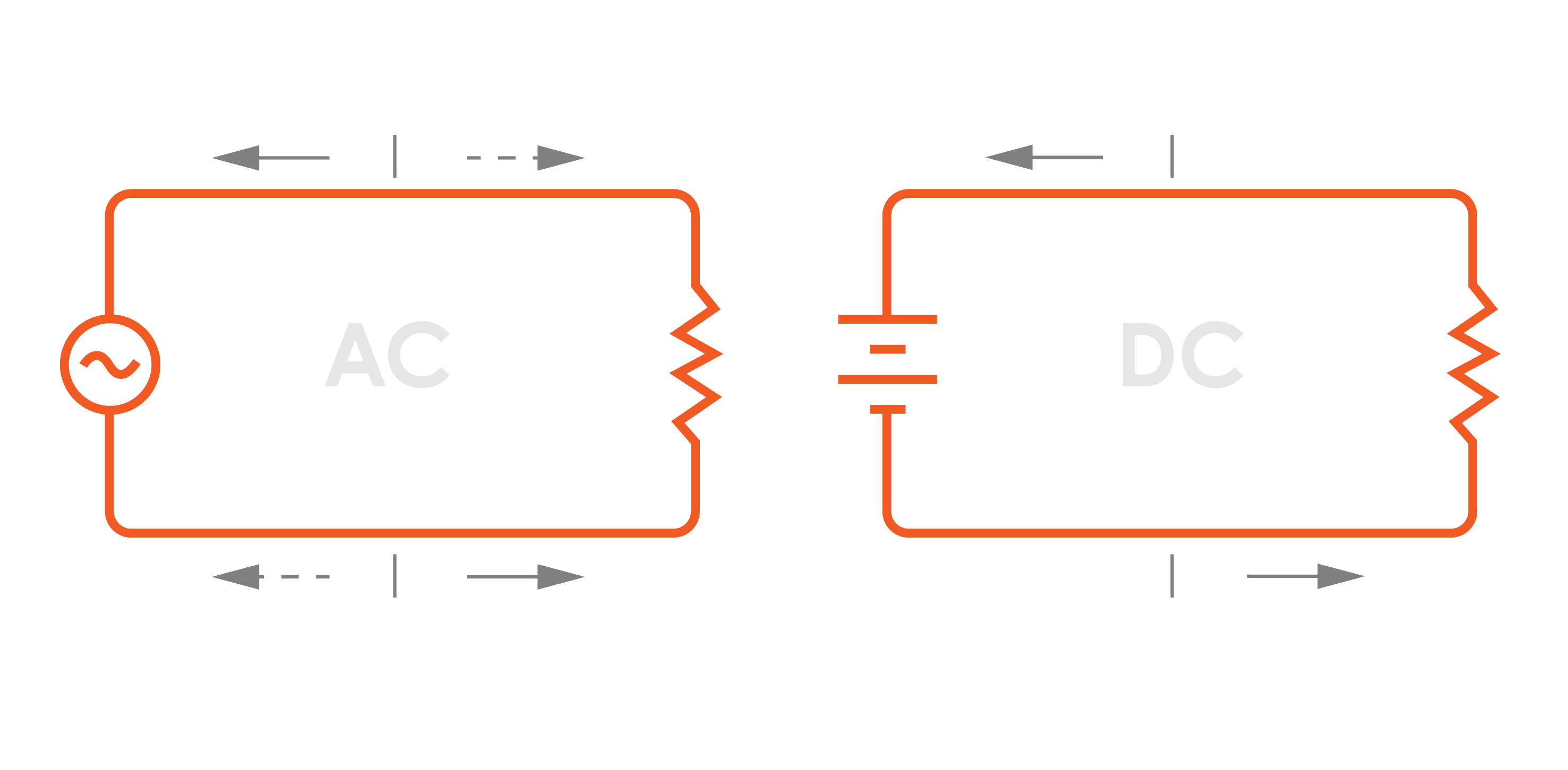
DC stands for Direct Current. It refers to the supply
and transmission of electrical
energy in which the flow of
electric charge is unidirectional,
maintaining a constant polarity.
In DC power, the voltage and
current flow in a single direction,
typically from a power source
or battery to an electrical
load. Unlike AC (Alternating
Current) power, which reverses
its direction of flow, 50 times a
second, DC power maintains
a steady flow of current in one
direction. This characteristic
makes it suitable for various
electronic devices, such as
computers, smartphones,
and automotive systems, that
require a stable and consistent
power supply.
DC power is commonly used in
applications where a constant
voltage or current is needed,
such as in battery-operated
devices, solar power systems
generate DC power, and some
industrial processes. It is also
used for transmitting power
over long distances through
high-voltage DC transmission
lines, known as HVDC (High-
Voltage Direct Current) lines,
which are more efficient than
AC transmission lines for certain
scenarios.
/ / WHAT IS AC POWER?
AC stands for Alternating Current. It refers to the supply and
transmission of electrical energy
in which the direction of electric
charge changes 50 times a
second. In AC power, the
voltage and current alternate
in direction and magnitude,
typically following a sinusoidal
waveform.
AC generators, such as
alternators, convert mechanical
energy into electrical energy.
The most common frequency
for AC power is 50 or 60 Hz
(hertz), indicating the number of
complete cycles per second.
AC power has several
advantages over DC
power. It allows for easy
voltage transformation using
transformers, which traditionally
enabled efficient transmission of
electricity over long distances.
AC is also suitable for powering
a wide range of electrical
devices, as it can be easily
converted to different voltages
using transformers and stepped
down using power supplies.
AC power is used for residential
and commercial electrical
systems, providing electricity to
homes, offices, and industries.
It is also the standard form of
power delivered through power
grids and is commonly used to
operate appliances, lighting
systems, motors, and other large
electronic devices.
/ / EXAMPLES
Examples uses of AC power:
Examples uses of DC power:
- Large home appliances (Fridge, freezer etc.)
- Industrial appliances
- Fans
- Toasters
- Pumps
Examples uses of DC power:
- Anything that’s powered by a battery (such as the QIKPAC CARRY)
- Mobile phones
- Solar power (up until an inverter)
- Laptops

As renewable power, in the
form of solar and wind farms,
becomes more prevalent
throughout the world, ways of
powering our commercial office
world with DC will become more
common. It is already possible to
power an entire workspace with
renewable DC power through
the use of microgrids and
batteries.
// SAVE FOR LATER – DOWNLOAD THE PDF
Click the button below to download this content in a PDF format.
questions?
GET IN TOUCH
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
more from OE
Hybrid meeting rooms: smart meeting rooms for hybrid working. read more >>